How Time-Restricted Eating affects leaky gut and systemic inflammation | Satchin Panda
Get the full length version of this episode as a podcast.
This episode will make a great companion for a long drive.
The Omega-3 Supplementation Guide
A blueprint for choosing the right fish oil supplement — filled with specific recommendations, guidelines for interpreting testing data, and dosage protocols.
In this clip, Dr. Satchidananda Panda of the Salk Institute touches on a lot of material but focuses on the practical implementation of time-restricted eating, featuring a few of the most frequent questions that came after our first conversation on FMF. Dr. Panda discusses the effects of time-restricted feeding on systemic inflammation; time-restricted eating as an opportunity for night-time repair that may prevent intestinal hyperpermeability (i.e., leaky gut), a primary source of systemic inflammation; and how the timing of macronutrients may differentially affect gut permeability.
This transcript is reserved for members.
FoundMyFitness Members get access to exclusive content not available anywhere else, including a transcript of this episode.
You wouldn't believe how cool being a premium member of the world's best cross-disciplinary science-focused website and podcast really is.
An organism’s ability to maintain its internal environment within defined limits that allow it to survive. Homeostasis involves self-regulating processes that return critical bodily systems to a particular “set point” within a narrow range of operation, consistent with the organism’s survival.
Experimental evidence from animal models links gut flora, an increase in intestinal permeability and endotoxemia of intestinal origin to low-grade chronic inflammation and obesity in animals.
Restricting the timing of food intake to certain hours of the day (typically within an 8- to 12-hour time window that begins with the first food or non-water drink) without an overt attempt to reduce caloric intake. TRE is a type of intermittent fasting. It may trigger some beneficial health effects, such as reduced fat mass, increased lean muscle mass, reduced inflammation, improved heart function with age, increased mitochondrial volume, ketone body production, improved repair processes, and aerobic endurance improvements. Some of these effects still need to be replicated in human trials.
Member only extras:
Learn more about the advantages of a premium membership by clicking below.
Get email updates with the latest curated healthspan research
Support our work
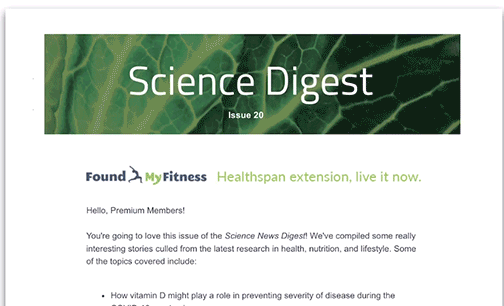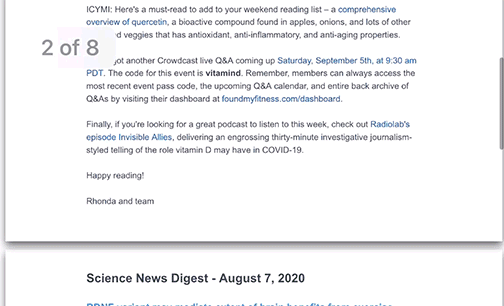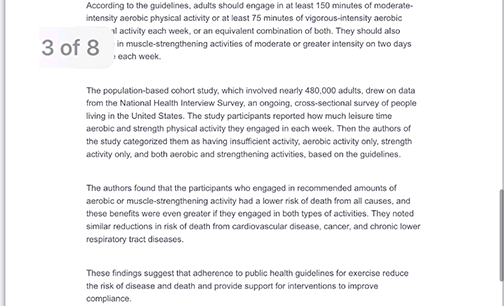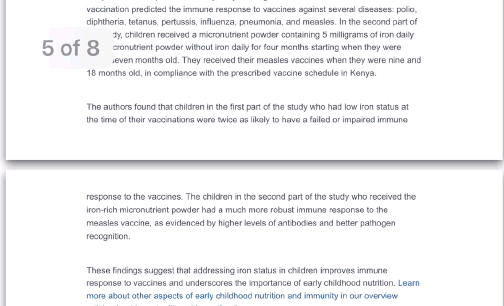
Every other week premium members receive a special edition newsletter that summarizes all of the latest healthspan research.
Time-restricted eating News
- Time-restricted eating helps lose weight without compromising sleep, mood, or quality of life, regardless of when the eating window occurs.
- Fasting-based dietary strategies, including intermittent fasting and time-restricted eating, show slight superiority over calorie restriction for promoting weight loss and improving insulin sensitivity.
- Late-night eating increases the risk of death from diabetes by as much as 131 percent.
- What are the optimal time-restricted eating patterns for cardiovascular wellness?
- Time-restricted eating decreases inflammation and leptin — a hormone that regulates food intake.





