How exposure to light in the evening affects mood and the circadian clock | Satchin Panda
Get the full length version of this episode as a podcast.
This episode will make a great companion for a long drive.
The Omega-3 Supplementation Guide
A blueprint for choosing the right fish oil supplement — filled with specific recommendations, guidelines for interpreting testing data, and dosage protocols.
Modern environments interfere with normal brain signals that induce sleep. For example, daytime work environments are often low light, inducing sleepiness. But bright lights from televisions or shift work environments in the evening or nighttime impair the release of melatonin, a hormone that promotes sleep, inducing wakefulness. The end result is an upside-down sleep schedule in which circadian rhythms and gene expression in the body become desynchronized. In this clip, Dr. Satchin Panda describes the effects of inappropriate light signals and discusses strategies to mitigate their effects.
This transcript is reserved for members.
FoundMyFitness Members get access to exclusive content not available anywhere else, including a transcript of this episode.
You wouldn't believe how cool being a premium member of the world's best cross-disciplinary science-focused website and podcast really is.
A wavelength of light emitted from natural and electronic sources. Blue light exposure is associated with improved attention span, reaction time, and mood. However, exposure to blue light outside the normal daytime hours may suppress melatonin secretion, impairing sleep patterns. In addition, blue light contributes to digital eye strain and may increase risk of developing macular degeneration.
The body’s 24-hour cycles of biological, hormonal, and behavioral patterns. Circadian rhythms modulate a wide array of physiological processes, including the body’s production of hormones that regulate sleep, hunger, metabolism, and others, ultimately influencing body weight, performance, and susceptibility to disease. As much as 80 percent of gene expression in mammals is under circadian control, including genes in the brain, liver, and muscle.[1] Consequently, circadian rhythmicity may have profound implications for human healthspan.
- ^ Dkhissi-Benyahya, Ouria; Chang, Max; Mure, Ludovic S; Benegiamo, Giorgia; Panda, Satchidananda; Le, Hiep D., et al. (2018). Diurnal Transcriptome Atlas Of A Primate Across Major Neural And Peripheral Tissues Science 359, 6381.
The process in which information stored in DNA is converted into instructions for making proteins or other molecules. Gene expression is highly regulated. It allows a cell to respond to factors in its environment and involves two processes: transcription and translation. Gene expression can be turned on or off, or it can simply be increased or decreased.
A hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle in mammals. Melatonin is produced in the pineal gland of the brain and is involved in the expression of more than 500 genes. The greatest influence on melatonin secretion is light: Generally, melatonin levels are low during the day and high during the night. Interestingly, melatonin levels are elevated in blind people, potentially contributing to their decreased cancer risk.[1]
- ^ Feychting M; Osterlund B; Ahlbom A (1998). Reduced cancer incidence among the blind. Epidemiology 9, 5.
Member only extras:
Learn more about the advantages of a premium membership by clicking below.
Get email updates with the latest curated healthspan research
Support our work
Every other week premium members receive a special edition newsletter that summarizes all of the latest healthspan research.
Circadian rhythm News
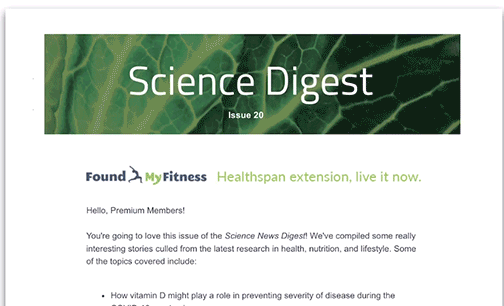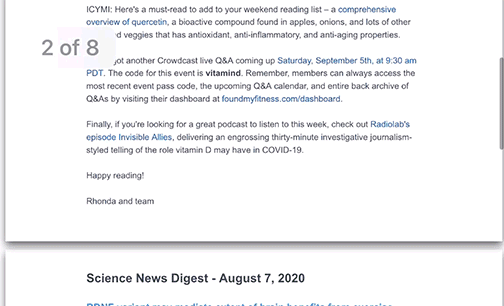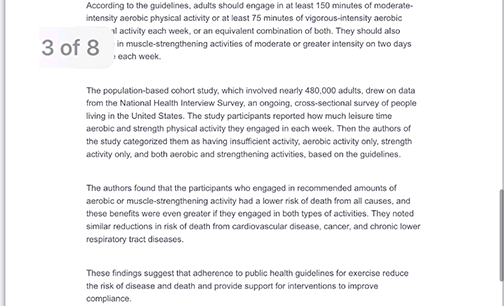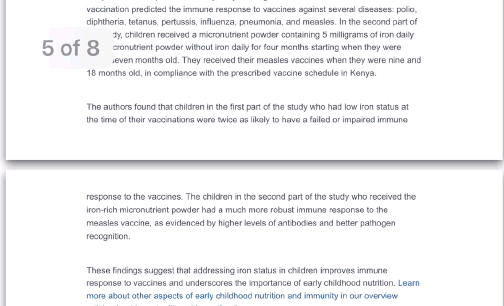
- Natural daylight during office hours improved blood sugar stability and shifted fuel use toward fat in adults with type 2 diabetes.
- Immunochemotherapy given earlier in the day linked to longer survival in people with advanced small cell lung cancer.
- Long-term exposure to bright, artificial night light linked to increased risk of overweight and obesity in schoolchildren.
- Regular cannabis use during adolescence may be linked to long-term insomnia risk.
- Consistency in daily activity rhythms can enhance cardiorespiratory fitness and walking efficiency up to 20% in older adults.






